More than 2,500 participants in this year’s Global PyTorch Summer Hackathon pushed the envelope to create unique new tools and applications for PyTorch developers and researchers.

Notice: None of the projects submitted to the hackathon are associated with or offered by Facebook, Inc.
This year’s projects fell into three categories:
-
PyTorch Developer Tools: a tool or library for improving productivity and efficiency for PyTorch researchers and developers.
-
Web/Mobile Applications Powered by PyTorch: a web or mobile interface and/or an embedded device built using PyTorch.
-
PyTorch Responsible AI Development Tools: a tool, library, or web/mobile app to support researchers and developers in creating responsible AI that factors in fairness, security, privacy, and more throughout its entire development process.
The virtual hackathon ran from June 22 to August 25, with more than 2,500 registered participants, representing 114 countries from Republic of Azerbaijan, to Zimbabwe, to Japan, submitting a total of 106 projects. Entrants were judged on their idea’s quality, originality, potential impact, and how well they implemented it.
Meet the winners of each category below.
PyTorch Developer Tools
1st place - DeMask
DeMask is an end-to-end model for enhancing speech while wearing face masks — offering a clear benefit during times when face masks are mandatory in many spaces and for workers who wear face masks on the job. Built with Asteroid, a PyTorch-based audio source separation toolkit, DeMask is trained to recognize distortions in speech created by the muffling from face masks and to adjust the speech to make it sound clearer.
This submission stood out in particular because it represents both a high-quality idea and an implementation that can be reproduced by other researchers.
Here is an example on how to train a speech separation model in less than 20 lines:
from torch import optim
from pytorch_lightning import Trainer
from asteroid import ConvTasNet
from asteroid.losses import PITLossWrapper
from asteroid.data import LibriMix
from asteroid.engine import System
train_loader, val_loader = LibriMix.loaders_from_mini(task='sep_clean', batch_size=4)
model = ConvTasNet(n_src=2)
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
loss = PITLossWrapper(
lambda x, y: (x - y).pow(2).mean(-1), # MSE
pit_from="pw_pt", # Point in the pairwise matrix.
)
system = System(model, optimizer, loss, train_loader, val_loader)
trainer = Trainer(fast_dev_run=True)
trainer.fit(system)
2nd place - carefree-learn
A PyTorch-based automated machine learning (AutoML) solution, carefree-learn provides high-level APIs to make training models using tabular data sets simpler. It features an interface similar to scikit-learn and functions as an end-to-end end pipeline for tabular data sets. It automatically detects feature column types and redundant feature columns, imputes missing values, encodes string columns and categorical columns, and preprocesses numerical columns, among other features.
3rd Place - TorchExpo
TorchExpo is a collection of models and extensions that simplifies taking PyTorch from research to production in mobile devices. This library is more than a web and mobile application, and also comes with a Python library. The Python library is available via pip install and it helps researchers convert a state-of-the-art model in TorchScript and ONNX format in just one line.
Web/Mobile Applications Powered by PyTorch
1st place - Q&Aid
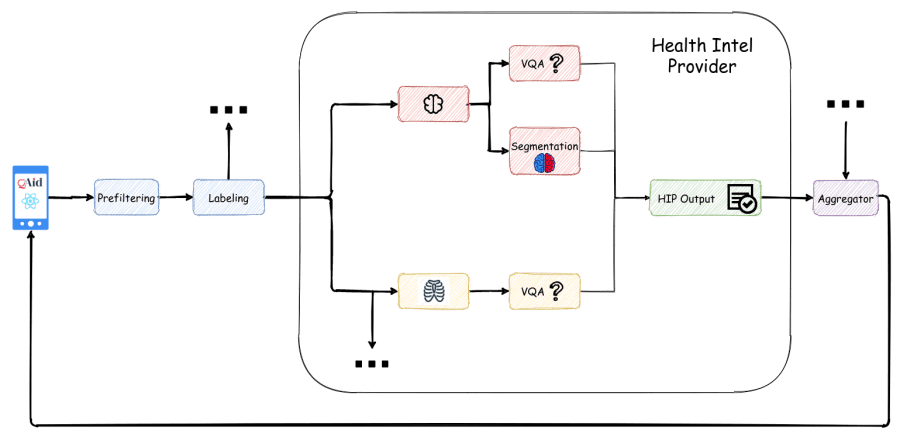
Q&Aid is a conceptual health-care chatbot aimed at making health-care diagnoses and facilitating communication between patients and doctors. It relies on a series of machine learning models to filter, label, and answer medical questions, based on a medical image and/or questions in text provided by a patient. The transcripts from the chat app then can be forwarded to the local hospitals and the patient will be contacted by one of them to make an appointment to determine proper diagnosis and care. The team hopes that this concept application helps hospitals to work with patients more efficiently and provide proper care.
2nd place - Rasoee
Rasoee is an application that can take images as input and output the name of the dish. It also lists the ingredients and recipe, along with the link to the original recipe online. Additionally, users can choose a cuisine from the list of cuisines in the drop menu, and describe the taste and/or method of preparation in text. Then the application will return matching dishes from the list of 308 identifiable dishes. The team has put a significant amount of effort gathering and cleaning various datasets to build more accurate and comprehensive models. You can check out the application here.
3rd place - Rexana the Robot — PyTorch
Rexana is an AI voice assistant meant to lay the foundation for a physical robot that can complete basic tasks around the house. The system is capable of autonomous navigation (knowing its position around the house relative to landmarks), recognizing voice commands, and object detection and recognition — meaning it can be commanded to perform various household tasks (e.g., “Rexana, water the potted plant in the lounge room.”). Rexana can be controlled remotely via a mobile device, and the robot itself features customizable hands (magnets, grippers, etc.) for taking on different jobs.
PyTorch Responsible AI Development Tools
1st place: FairTorch
FairTorch is a fairness library for PyTorch. It lets developers add constraints to their models to equalize metrics across subgroups by simply adding a few lines of code. Model builders can choose a metric definition of fairness for their context, and enforce it at time of training. The library offers a suite of metrics that measure an AI system’s performance among subgroups, and can apply to high-stakes examples where decision-making algorithms are deployed, such as hiring, school admissions, and banking.
2nd place: Fluence
Fluence is a PyTorch-based deep learning library for language research. It specifically addresses the large compute demands of natural language processing (NLP) research. Fluence aims to provide low-resource and computationally efficient algorithms for NLP, giving researchers algorithms that can enhance current NLP methods or help discover where current methods fall short.
3rd place: Causing: CAUSal INterpretation using Graphs
Causing (CAUSal INterpretation using Graphs) is a multivariate graphic analysis tool for bringing transparency to neural networks. It explains causality and helps researchers and developers interpret the causal effects of a given equation system to ensure fairness. Developers can input data and a model describing the dependencies between the variables within the data set into Causing, and Causing will output a colored graph of quantified effects acting between the model’s variables. In addition, it also allows developers to estimate these effects to validate whether data fits a model.
Thank you,
The PyTorch team
